ICYMI: Science and technology updates from April 28 to May 4, 2019.
DENR and Couples for Christ agree to plant 1 million trees
From Rappler:
The Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) signed a memorandum of agreement with Catholic group Couples for Christ (CFC) to plant one million trees.
In a statement on Sunday, April 28, the DENR said CFC will plant one million forest tree seedlings from 2019 to 2021. The group will also be tasked with “maintaining and protecting the planted seedlings during that period.”
On the part of the DENR, it will identify the forestlands where the seedlings will be planted and which tree species should be planted.
UK scientists find traces of illegal drugs in shrimp
From CNN:
Researchers in the UK have found traces of illicit drugs, pharmaceuticals and pesticides in samples of freshwater shrimp.
A study carried out by scientists from King’s College London and the University of Suffolk tested the exposure of wildlife like freshwater shrimp to different micropollutants at 15 different sites in the county of Suffolk.
Scientists were surprised to find illicit drugs in samples in rural England, with cocaine found in all samples tested and ketamine also widespread.
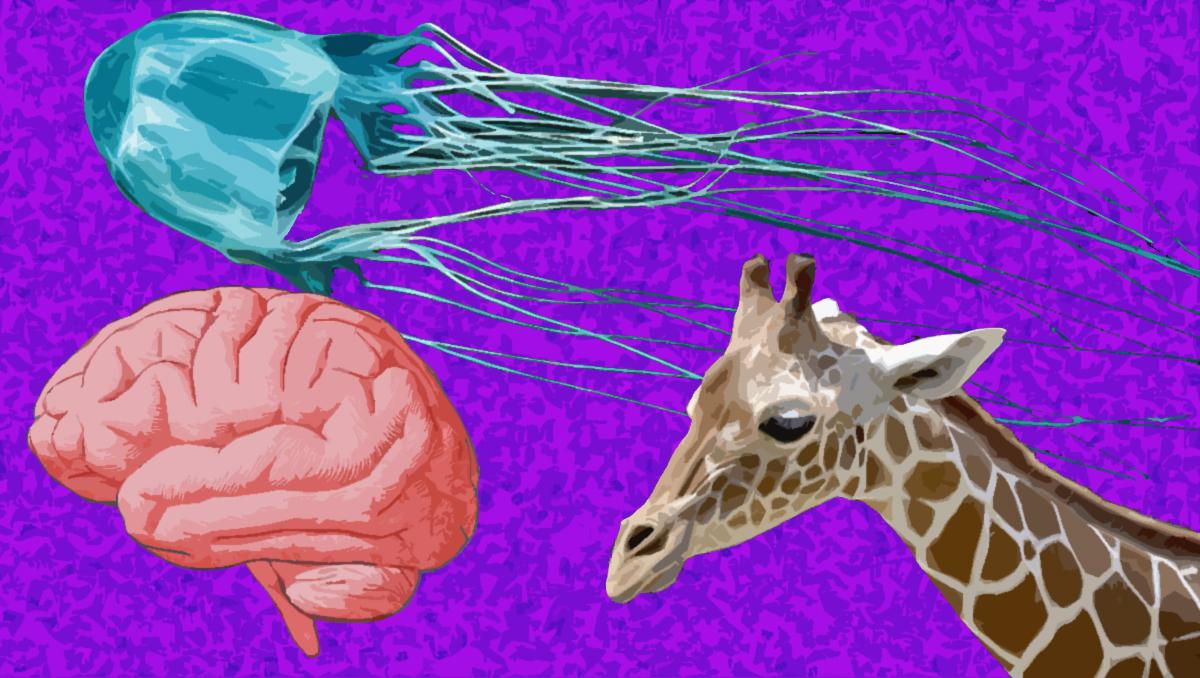
Next on the endangered species list: Giraffes?

From CNN:
The United States is considering giving new protection to giraffes, whose numbers have dropped dramatically in recent decades.
The US Fish and Wildlife Service announced last week that it will conduct an in-depth review on whether to add the species to the list of endangered and threatened wildlife under the Endangered Species Act.
The petition to protect giraffes, which was filed by a coalition of conservation groups in April 2017, says the animals are “in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of its range.”
The world’s biggest ice shelf is melting 10 times faster than expected
From Phys.org:
Scientists have discovered that ocean water warmed by the sun is melting part of the world’s largest ice shelf 10 times faster than the overall average.
The north-west sector of the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica, which in total is roughly the size of France, is melting far faster than scientists previously thought, according to a press release from the University of Cambridge.
And scientists have identified an unlikely culprit: inflowing warm water from the ocean’s surface.
New type of Alzheimer’s-like brain degeneration identified

From TIME.com:
Some people told they have Alzheimer’s may instead have a newly identified mimic of the disease — and scientists say even though neither is yet curable, it’s critical to get better at telling different kinds of dementia apart.
Too often, the word dementia is used interchangeably with Alzheimer’s when there are multiple types of brain degeneration that can harm people’s memory and thinking skills.
It’s not clear how many people have this particular type, which an international team of scientists defined Tuesday in the journal Brain. But there could be a sizeable number, said Dr. Peter Nelson of the University of Kentucky, the paper’s lead author.
The dementia was dubbed “LATE,” an acronym chosen in part because the oldest seniors seem at greatest risk.
Researchers may have found antidote for deadly jellyfish venom

From Science:
The sting of a box jellyfish can kill a person in minutes. But scientists have long been at pains to figure out the secret of its fast-acting venom, which can also cause severe agony, inflammation, and heart attacks. A new study may have the answer—and a potential antidote.